Cohort-Based Spatial Similarity Can Predict Radiotherapy Dose Distribution
September 15th, 2019
Categories: Applications, Software, Visual Analytics, Visual Informatics, Human Computer Interaction (HCI)
Authors
Wentzel, A., Elgohari, B., Hanula, P., Luciani, T., Elhalawani, H., Cardenas, C.E., Edwards, B., Mohamed, A.S., Canahuate, G., Vock, D., Fuller, C.D., Marai, G.E.About
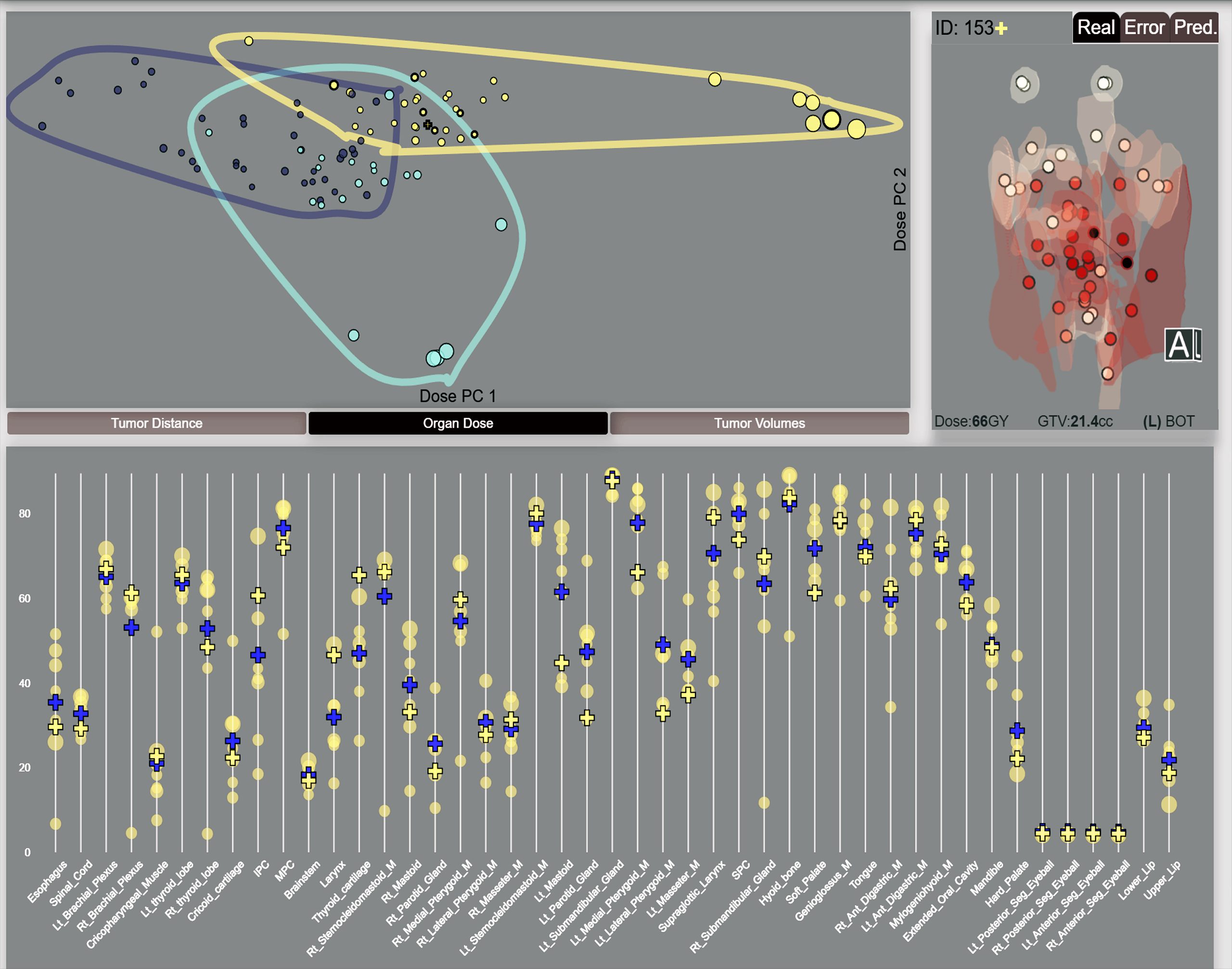
In head and neck (HN) cancer treatment, radiotherapy (RT) plans assigned to a given patient depend in large measure on the tumor location with respect to surrounding organs at risk (OARs). With the emergence of Big Data repositories, RT data from patients with
similar tumor locations could be used to predict the RT plan for a new patient, as opposed to clinicians or institutional memory alone.
We propose an automated technique to evaluate RT plan similarity between HN cancer patients who have previously received radiotherapy, based on similarities in their tumor location with respect to OARs. We use this technique to predict and evaluate the RT dose distribution across organs in a new HN patient, using similar patients as a prior.
Funding: NIH Award #NCI-R01CA225190: QuBBD: Precision E –Radiomics for Dynamic Big Head & Neck Cancer Data (Marai, PI)
NIH, National Cancer Institute #1R01CA214825-01: SMART-ACT: Spatial Methodologic Approaches for Risk Assessment and Therapeutic Adaptation in Cancer Treatment (Marai, PI)
Resources
Citation
Wentzel, A., Elgohari, B., Hanula, P., Luciani, T., Elhalawani, H., Cardenas, C.E., Edwards, B., Mohamed, A.S., Canahuate, G., Vock, D., Fuller, C.D., Marai, G.E., Cohort-Based Spatial Similarity Can Predict Radiotherapy Dose Distribution, ASTRO Annual Meeting of the American Society for Radiation Oncology, Chicago, IL, pp. 1-2, September 15th, 2019.