Correlating Toxicity Outcomes with Spatial Patterns of Lymph Node Metastasis for Oropharyngeal Cancer Patients
September 15th, 2019
Categories: Applications, Software, User Groups, Visual Analytics, Visual Informatics, Human Computer Interaction (HCI)
Authors
Luciani,T., Elgohari, B., Elhalawani, H., Mohamed, A.S., Canahuate, G., Vock, D., Fuller, C.D., Marai, G.E.About
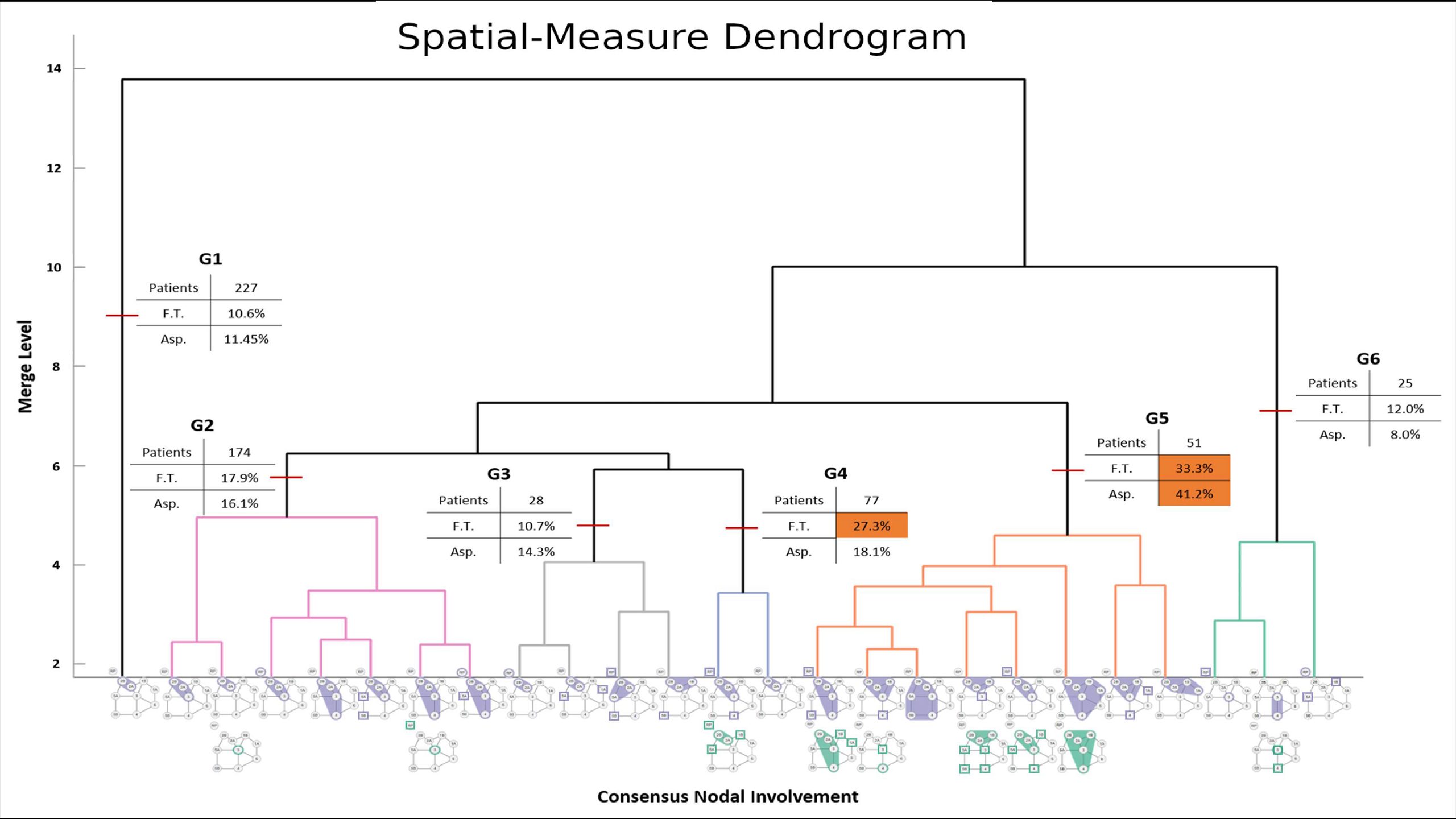
Imaging is an integral tool in radiation oncology, starting from initial diagnosis to follow-up post-therapy. In head and neck
cancer treatment, toxicity and tumor control depend on the tumor locational geometry and systematic predictable spread of disease to
affected lymph nodes (LN) levels. However, a rigorous methodology for integrating imaging spatial information into treatment outcome
prediction models remains an unmet need. We hypothesized that integrating tumor and LN spatial information derived from routine diagnostic images can aid in prediction model development for both oncologic outcomes and post-therapy toxicity.
Funding: NIH Award #NCI-R01CA225190: QuBBD: Precision E –Radiomics for Dynamic Big Head & Neck Cancer Data (Marai, PI)
NIH, National Cancer Institute #1R01CA214825-01: SMART-ACT: Spatial Methodologic Approaches for Risk Assessment and Therapeutic Adaptation in Cancer Treatment (Marai, PI)
Resources
Citation
Luciani,T., Elgohari, B., Elhalawani, H., Mohamed, A.S., Canahuate, G., Vock, D., Fuller, C.D., Marai, G.E., Correlating Toxicity Outcomes with Spatial Patterns of Lymph Node Metastasis for Oropharyngeal Cancer Patients, ASTRO Annual Meeting of the American Society for Radiation Oncology, Chicago, IL, September 15th, 2019.