Cohort-based T-SSIM Visual Computing for Radiation Therapy Prediction and Exploration
August 22nd, 2019
Categories: Applications, Software, User Groups, Visual Analytics, Visual Informatics, Human Computer Interaction (HCI)
Authors
Wentzel, A., Hanula, P., Luciani, T,, Elgohary, B., Canahuate. G., Vock, D., Fuller, C.D., Marai, G.E.About
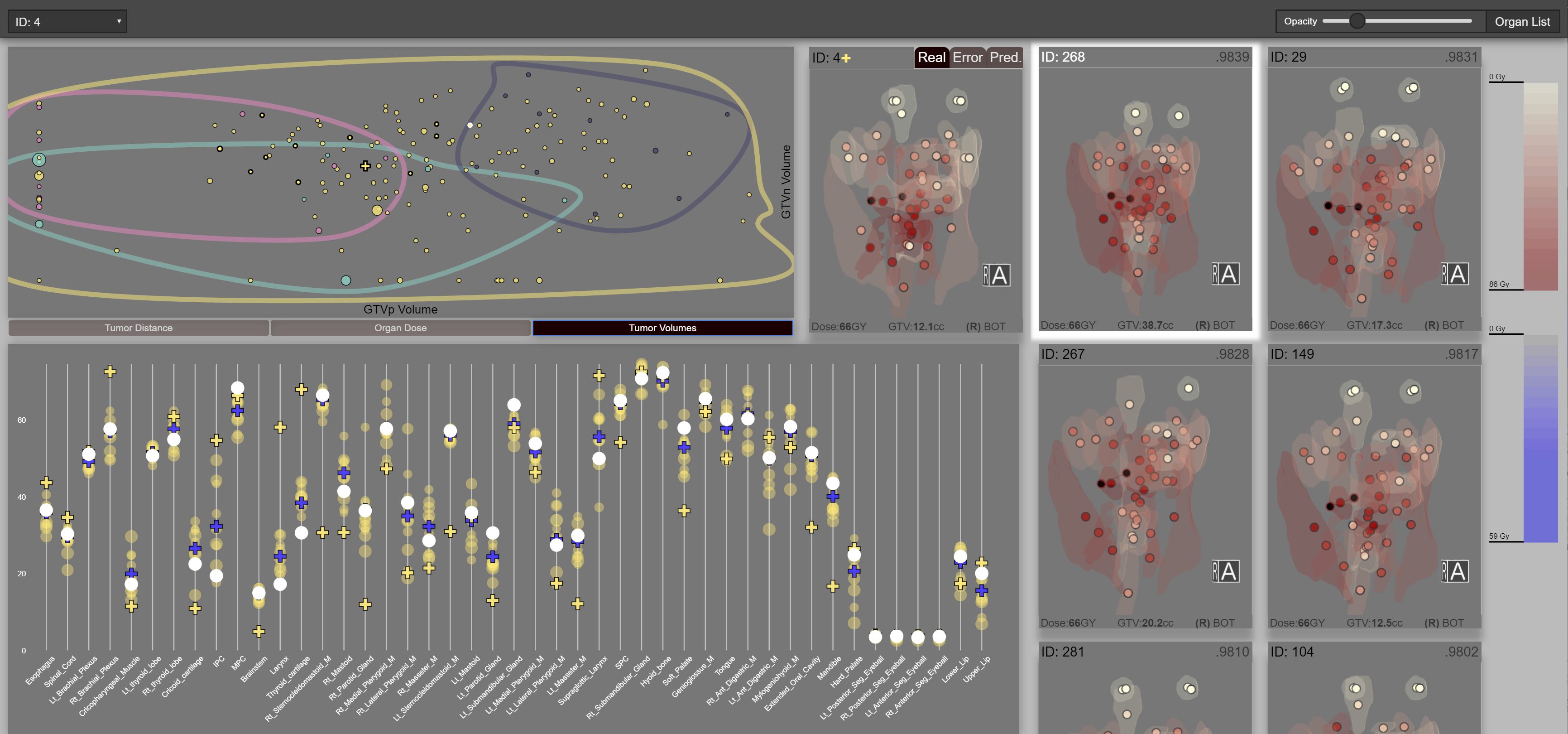
We describe a visual computing approach to radiation therapy (RT) planning, based on spatial similarity within a patient cohort. In radiotherapy for head and neck cancer treatment, dosage to organs at risk surrounding a tumor is a large cause of treatment toxicity. Along with the availability of patient repositories, this situation has lead to clinician interest in understanding and predicting RT outcomes based on previously treated similar patients. To enable this type of analysis, we introduce a novel topology-based spatial similarity measure, T-SSIM, and a predictive algorithm based on this similarity measure. We couple the algorithm with a visual steering interface that intertwines visual encodings for the spatial data and statistical results, including a novel parallel-marker encoding that is spatially aware. We report quantitative results on a cohort of 165 patients, as well as a qualitative evaluation with domain experts in radiation oncology, data management, biostatistics, and medical imaging, who are collaborating remotely.
Keywords: Biomedical and Medical Visualization, Spatial Techniques, Visual Design, High-Dimensional Data
Funding: NIH Award #NCI-R01CA225190: QuBBD: Precision E –Radiomics for Dynamic Big Head & Neck Cancer Data (Marai, PI)
NIH, National Cancer Institute #1R01CA214825-01: SMART-ACT: Spatial Methodologic Approaches for Risk Assessment and Therapeutic Adaptation in Cancer Treatment (Marai, PI)
Resources
URL
Citation
Wentzel, A., Hanula, P., Luciani, T,, Elgohary, B., Canahuate. G., Vock, D., Fuller, C.D., Marai, G.E., Cohort-based T-SSIM Visual Computing for Radiation Therapy Prediction and Exploration, IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, IEEE Vis 2019, pp. 1-11, August 22nd, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVCG.2019.2934546